Unremovable Friend Request
Introduction
The “Unremovable Friend Request” exploit was initially discovered in late 2020 by a user known as Saad. At the time, the vulnerability was not widely known, yet the development team was able to patch it within a week. Despite this, existing unremovable friend requests have remained persistent in the system.
Technical breakdown of the original exploit
The vulnerability stemmed from improper handling of friend-code string lengths in the game’s backend. Specifically:
- Users could set a
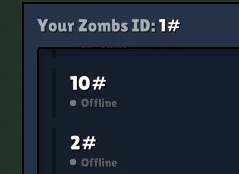
friend_codevalue that was excessively long, causing a buffer overflow in the friend system. - This overflow resulted in the removal of the identifier suffix (e.g.,
username#1234→username#), thereby corrupting the internal representation of the user tag. - If the overflow was too large, the system failed to process the friend-code, yet still allowed it to send friend requests.
- These requests became unremovable and unconfirmable on the recipient’s side, effectively leaving them in a persistent, unmanageable state.
Artifact

Patch & mitigation measures
The exploit was mitigated shortly after its discovery through a server-side input validation:
- A length constraint was introduced on the friend-code update request, effectively preventing overflow conditions.
- It is unclear whether any additional backend modifications were implemented to harden the system against similar future vulnerabilities.
Current status and future
As of writing this, the server-side check has been effective for over five years. However:
- In 2023, a new bypass method was privately rediscovered, but has not been publicly disclosed.
- This updated method has only been shared among trusted individuals, and the developers remain unaware of its existence.
- Given the developers’ historical response time, a silent patch could be expected once the new bypass becomes known internally.